As the team at Total Control Pro work closer with a number of Manufacturing consultants and partners to deliver our solution, we’ve realised they fall largely into two camps, the Lean Masters and the Agile Advocates, and it’s very helpful to understand this from the start of the software configurations and implementation stage.
Agile manufacturing and lean manufacturing are two different approaches to manufacturing processes that aim to increase efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity.
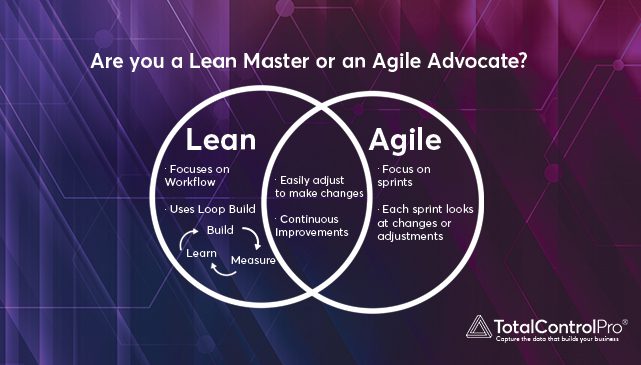
Agile manufacturing focuses on flexibility and responsiveness to changing customer needs and market conditions. It emphasizes collaboration, quick decision-making, and continuous improvement. The goal of agile manufacturing is to quickly and efficiently produce customized products that meet customer demand, without sacrificing quality.
On the other hand, lean manufacturing is an approach that aims to eliminate waste and optimize processes. It focuses on reducing non-value-added activities, such as overproduction, waiting, defects, overprocessing, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and unused talent. The goal of lean manufacturing is to create a smooth, efficient flow of materials and information through the production process, delivering products on time with minimum waste.
Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing requires a different approach from traditional manufacturing, as it emphasizes flexibility, speed, and responsiveness. To achieve this, several systems and practices can be put in place. Here are some examples:
- Modular Manufacturing: Modular manufacturing involves breaking down the production process into small, independent modules that can be easily combined to create different products. This approach allows for greater flexibility, as modules can be rearranged or replaced as needed.
- Rapid Prototyping: Rapid prototyping involves creating physical models of new products quickly and inexpensively. This approach allows for fast iteration and testing, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in customer needs or market conditions.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Cross-functional teams bring together individuals from different departments or areas of expertise to work together on a project. This approach encourages collaboration and knowledge-sharing, enabling teams to quickly identify and solve problems.
- Just-In-Time Manufacturing: Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing involves producing products only as they are needed, rather than building up a large inventory. This approach reduces waste and frees up resources for other tasks.
- Agile Supply Chains: Agile supply chains are designed to be flexible and responsive, with the ability to quickly adjust to changes in demand or supply. This approach involves working closely with suppliers and customers to ensure that materials and products are delivered on time and to the required quality standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement involves constantly analysing and improving processes to eliminate waste, reduce costs, and improve quality. This approach requires a culture of experimentation and innovation, with a focus on learning from mistakes and making incremental improvements over time.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is an approach that aims to eliminate waste and optimize processes to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality. To achieve these goals, several systems and practices can be put in place. Here are some examples:
- Kanban System: Kanban is a Japanese term that means “visual signal.” A Kanban system is a pull-based system that uses visual signals, such as cards or bins, to signal the need for materials or parts. This approach ensures that materials are delivered just in time, reducing inventory and waste.
- Value Stream Mapping: Value stream mapping involves analysing the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished products, to identify non-value-added activities and opportunities for improvement. This approach helps to identify and eliminate waste, reduce lead times, and improve overall efficiency.
- Single-Piece Flow: Single-piece flow involves producing one item at a time, rather than in batches. This approach reduces inventory and waiting times while improving quality and reducing defects.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): TPM is a system that involves regular maintenance and inspection of equipment to reduce downtime and improve productivity. This approach helps to identify and eliminate equipment-related waste, such as breakdowns or defects.
- 5S System: 5S is a workplace organization system that involves sorting, simplifying, sweeping, standardizing, and sustaining. This approach helps to create a clean and organized work environment, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Poka-Yoke: Poka-yoke is a Japanese term that means “mistake-proofing.” This approach involves designing processes and equipment to prevent errors or defects from occurring. This approach helps to improve quality, reduce waste, and minimize the need for rework or inspection.
Conclusion
In summary, while both agile and lean manufacturing aims to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity, they differ in their approach. Agile manufacturing emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness, while lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process optimization. Ultimately, the best approach will depend on the specific needs and goals of the manufacturing organization.
At Total Control Pro, we use an Agile software process to deliver our DynamxMFG platform, we know that there are features and configurations that best serve Lean, while others best serve Agile. If you are looking to implement new technology to support your manufacturing process, contact us to discuss these variations.
New to TotalControlPro and have a question?
Just fill in the form below and we’ll get back to you as quickly as possible.



